How to Use the VxLang SDK
This page explains how to use the VxLang SDK to perform code obfuscation.
How to Build the SDK Code
The path to the SDK source code and msvc-project is as follows:
Configuring the SDK is very simple. You can export the VxLang API as follows.
extern "C"
void VxVirtualizationBegin() {
return;
}
extern "C"
void VxVirtualizationEnd() {
return;
}
//
extern "C"
void VxDualModeBegin() {
return;
}
extern "C"
void VxDualModeEnd() {
return;
}
//
extern "C"
void VxObfuscationBegin() {
return;
}
extern "C"
void VxObfuscationEnd() {
return;
}
//
extern "C"
void VxCodeFlatteningBegin() {
return;
}
extern "C"
void VxCodeFlatteningEnd() {
return;
}
These functions are defined by the following macros:
#define VL_OBFUSCATION_BEGIN VxObfuscationBegin()
#define VL_OBFUSCATION_END VxObfuscationEnd()
#define VL_CODE_FLATTENING_BEGIN VxCodeFlatteningBegin()
#define VL_CODE_FLATTENING_END VxCodeFlatteningEnd()
#define VL_VIRTUALIZATION_BEGIN VxVirtualizationBegin()
#define VL_VIRTUALIZATION_END VxVirtualizationEnd()
#define VL_DUAL_MODE_BEGIN VxDualModeBegin()
#define VL_DUAL_MODE_END VxDualModeEnd()
By applying this SDK as shown in the example below, you can specify the desired code and sections to protect using VxLang.
void test() {
VL_OBFUSCATION_BEGIN;
printf("Hello Wolrd ! \n");
VL_OBFUSCATION_END;
return;
}
How to Review the Obfuscation
By default, VxLang performs protection through binary packing and obfuscation using VxLang-Core.
Therefore, to verify code obfuscation, the VxLang core should be excluded using the following command.
To check if your code is obfuscated, you can use --disable-core.
TIP
vxlang.exe ${Your-Binary} –disable-core
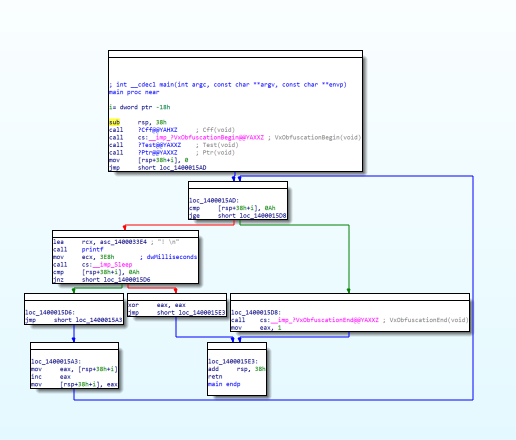
If you use the code-flattening SDK, you can view the obfuscated code as shown in the figure below:
- Before:
- After:
Precautions
When applying code obfuscation, you must anticipate the code generated by the compiler and carefully manage the optimization process. Therefore, in this section, we will examine the critical points to watch out for and learn how to work around them.
Compiler Optimization Considerations
When compiler optimizations are enabled, unnecessary code may be removed or repeated code may be merged depending on user settings. If this happens to code where the VxLang SDK is applied, it may cause issues in program execution. Therefore, it is recommended to disable optimization only for the relevant code or code section during the SDK application process, as shown below.
#pragma optimize("", off) // turn off optimization ..
void ObfuscationTest() {
VL_OBFUSCATION_BEGIN;
// ...
VL_OBFUSCATION_END;
return;
}
Jump Table-Based Branch Transition
User-written code may sometimes generate table-based branch transitions instead of the specified locations. Just like in the codes shown below:
jmp reg
jmp [reg+reg+offset]
...
call _VXLANG_BEGIN
jmp L1
L0:
jmp EXIT
L1:
lea rax, $L0
jmp rax
EXIT:
call _VXLANG_END
...
In such cases, a jump table is set up somewhere in the code, and branching occurs through it. A representative example of code that generates this behavior is the switch-case statement.
#pragma optimize("", off)
void Warning_SwitchCaseTest(int value) {
switch (value) {
case 1:
std::cout << " Case 1" << std::endl;
break;
case 2:
std::cout << " Case 2" << std::endl;
break;
case 3:
std::cout << " Case 3" << std::endl;
break;
case 4:
std::cout << " Case 4" << std::endl;
break;
case 5:
std::cout << " Case 5" << std::endl;
break;
case 6:
std::cout << " Case 6" << std::endl;
break;
case 7:
std::cout << " Case 7" << std::endl;
break;
case 8:
std::cout << " Case 8" << std::endl;
break;
case 9:
std::cout << " Case 9" << std::endl;
break;
case 10:
std::cout << " Case 10" << std::endl;
break;
case 11:
std::cout << " Case 11" << std::endl;
break;
case 12:
std::cout << " Case 12" << std::endl;
break;
case 13:
std::cout << " Case 13" << std::endl;
break;
case 14:
std::cout << " Case 14" << std::endl;
break;
case 15:
std::cout << " Case 15" << std::endl;
break;
default:
std::cout << " Default" << std::endl;
break;
}
return;
}
For this type of code, it is recommended not to apply the SDK to the entire function block, but rather to apply it separately to each section.
#pragma optimize("", off)
void Warning_SwitchCaseTest(int value) {
switch (value) {
case 1:
VL_VIRTUALIZATION_BEGIN;
std::cout << " Case 1" << std::endl;
VL_VIRTUALIZATION_END;
break;
case 2:
VL_VIRTUALIZATION_BEGIN;
std::cout << " Case 2" << std::endl;
VL_VIRTUALIZATION_END;
break;
case 3:
VL_VIRTUALIZATION_BEGIN;
std::cout << " Case 3" << std::endl;
VL_VIRTUALIZATION_END;
break;
case 4:
VL_VIRTUALIZATION_BEGIN;
std::cout << " Case 4" << std::endl;
VL_VIRTUALIZATION_END;
break;
case 5:
VL_VIRTUALIZATION_BEGIN;
std::cout << " Case 5" << std::endl;
VL_VIRTUALIZATION_END;
break;
case 6:
VL_VIRTUALIZATION_BEGIN;
std::cout << " Case 6" << std::endl;
VL_VIRTUALIZATION_END;
break;
case 7:
VL_VIRTUALIZATION_BEGIN;
std::cout << " Case 7" << std::endl;
VL_VIRTUALIZATION_END;
break;
case 8:
VL_VIRTUALIZATION_BEGIN;
std::cout << " Case 8" << std::endl;
VL_VIRTUALIZATION_END;
break;
case 9:
VL_VIRTUALIZATION_BEGIN;
std::cout << " Case 9" << std::endl;
VL_VIRTUALIZATION_END;
break;
case 10:
VL_VIRTUALIZATION_BEGIN;
std::cout << " Case 10" << std::endl;
VL_VIRTUALIZATION_END;
break;
case 11:
VL_VIRTUALIZATION_BEGIN;
std::cout << " Case 11" << std::endl;
VL_VIRTUALIZATION_END;
break;
case 12:
VL_VIRTUALIZATION_BEGIN;
std::cout << " Case 12" << std::endl;
VL_VIRTUALIZATION_END;
break;
case 13:
VL_VIRTUALIZATION_BEGIN;
std::cout << " Case 13" << std::endl;
VL_VIRTUALIZATION_END;
break;
case 14:
VL_VIRTUALIZATION_BEGIN;
std::cout << " Case 14" << std::endl;
VL_VIRTUALIZATION_END;
break;
case 15:
VL_VIRTUALIZATION_BEGIN;
std::cout << " Case 15" << std::endl;
VL_VIRTUALIZATION_END;
break;
default:
VL_VIRTUALIZATION_BEGIN;
std::cout << " Default" << std::endl;
break;
}
return;
}
A real sample link for this can be found below:
Exception Handling
Exception handlers cause branch transitions triggered by the operating system running the process. A representative example is SEH (Structured Exception Handling), and VxLang officially supports SEH only. To apply it to SEH, simply apply the SDK to the entire block, as done previously.
#pragma optimize("", off)
void ObfuscationSEHTest() {
VL_OBFUSCATION_BEGIN;
__try {
printf("SEH Test \n");
__debugbreak();
}
__except (1) {
printf(" Except \n");
}
VL_OBFUSCATION_END;
return;
}
Compiler-Specific Exception Handling (C++/Rust/Etc.)
Language-level exception handling, such as in C++, is controlled through extended specifications rather than the system. This varies across compilers (MSVC, Clang, etc.). In such cases, it is recommended to apply the SDK as shown below to work around it. The important point is that the actual exception must be placed outside the SDK.
#pragma optimize("", off)
void test() {
try {
VL_OBFUSCATION_BEGIN;
printf(" > ObfuscationCxxEHTest \n");
VL_OBFUSCATION_END;
// *** Raise Exception
throw std::runtime_error("Something went wrong - 1");
}
catch (...) {
VL_OBFUSCATION_BEGIN;
printf(" > ObfuscationCxxEHTest Catch .. \n");
VL_OBFUSCATION_END;
}
return;
}
Exception handling for each compiler will be managed through VxLang plugins.